Kenya will look to criminalize doping in athletics
Kenyan Sports Minster Ababu Namwama hopes to send those responsible for doping to prison

In an attempt to crack down on doping, Kenyan Sports Minster Ababu Namwama told BBC News Africa that he hopes to fast-track modifications to legislation and crack down on doping the same way the government does with illegal drugs.
Last week, the East African country avoided a sanction by governing body World Athletics—despite having 55 athletes currently serving doping-related suspensions. Kenya has the third highest number of suspensions behind Russia (102) and India (61) and is categorized as one of the seven “Category A” nations threatening the overall integrity of the sport.

On Dec. 2, the Kenyan government reached an agreement with World Athletics to spend USD $25 million over the next five years to combat the war on doping, which will help pay for more anti-doping personnel, increase testing and investigation and strengthen education.
“I believe we need to criminalize doping and elevate the handling of doping substances to the same level [as] narcotics,” says Namwama. “Convicted dopers should be dealt with the way we deal with drug traffickers.”
According to Kenyan law, any person who is in possession of any narcotic drug is guilty of an offense and faces a fine of five million Kenyan shillings (USD $40,000) or imprisonment for up to five years. They may also be forced into a rehabilitation program for a minimum of six months.
France is one country that outlaws doping in sports with prison sentences and fines. In 2009, the government adopted a law that penalizes the possession and trafficking of doping products in sports. Offenders can receive up to five years in jail and a 75,000-euro fine. For more severe cases, the penalty may also be increased to seven years and a fine of 150,000 euros. If an athlete is found guilty of personal use, they can be sentenced to a year in prison and a 3,750-euro fine.
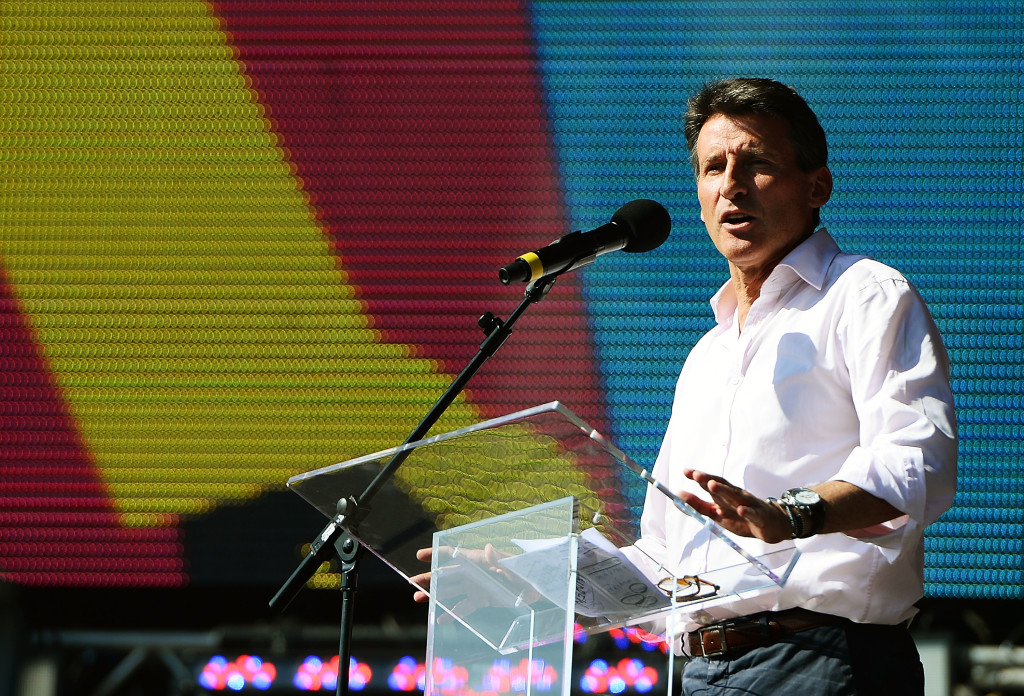

During a World Athletics Council meeting in Rome in November, WA president Sebastian Coe said Kenya faces “a long journey ahead” to regain the trust of the World Athletics.
Coe told BBC News Africa that he has no problems with Kenya criminalizing the trafficking of these substances, but pointed out that criminalizing athletes can be complicated.
Previous attempts to criminalize doping in Kenya have been unsuccessful, with a motion submitted by former member of parliament and 2012 Boston Marathon champion Wesley Korir being defeated in 2016. Korir and his wife Tarah Korir lived in Waterloo, Ont. for several years before moving back to Kenya.